The Emergence of AI based Autonomous UV Disinfection Robots in Pandemic Response and Hygiene Maintenance
Shivansh Khanna
Tennant Company; University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
Shraddha Srivastava
Micron Technology, Boise, ID
Keywords: Autonomous Navigation, Data Analysis and Reporting, Human Safety Measures, Real-Time Adaptation, Reduced Risk of Infection, Technical Limitations, UV Disinfection Technology
Abstract
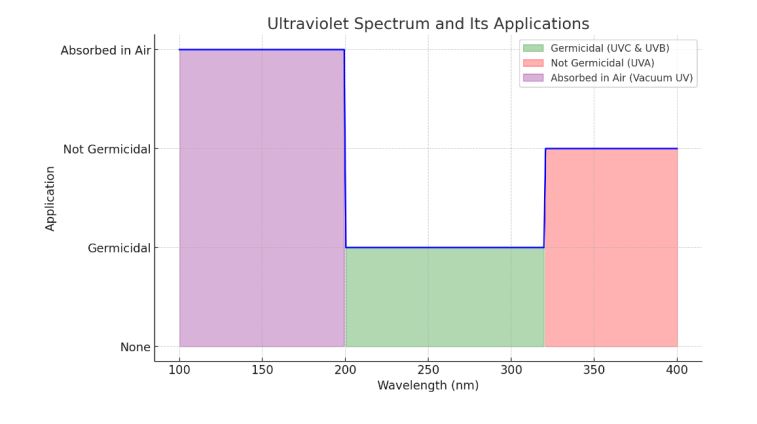
Traditional disinfection methods, often reliant on manual labor, are not only time-consuming but also pose health risks to the workers involved. Robots, on the other hand, offer a more efficient and safer alternative. This paper discusses the development and applications of AI-based autonomous UV disinfection robots, highlighting their opportunities in improving pandemic response and maintaining hygiene standards. These robots use ultraviolet (UV) light for its germicidal properties to mitigate the spread of pathogens. Firstly, the study discussed how the integration of AI in disinfection robots enables autonomous navigation, real-time environmental analysis, and operational adaptability, which, along with sensor-driven AI algorithms, allows the robots to maneuver effectively in varied environments, avoiding obstacles and human presence for efficient and thorough disinfection. The core of their functionality lies in the UV disinfection technology for pathogen reduction. These disinfection robots can adapt in real-time to environmental changes, optimizing the disinfection process, and are equipped with data analysis and reporting tools to assist in facility management and maintain hygiene standards. They follow safety through automatic shutoff to prevent human UV exposure, activating when people are detected. Secondly, the study explores the deployment of these robots in diverse settings, including healthcare facilities, public transportation, educational institutions, commercial spaces, and industrial environments. Their role in these sectors is important in mitigating healthcare-associated infections and maintaining high hygiene standards during pandemics. The research identifies several benefits, including increased efficiency, reduced infection risks, and minimal human intervention. Challenges such as high initial costs, technical limitations, and potential human job displacement are also discussed. This study argued that the future applications of UV disinfection robotics extend far beyond the current focus on COVID-19. UV robots could be vital in public health strategies against both current and emerging infectious diseases by enhancing disinfection protocols in healthcare and public spaces.
Author Biographies
Shivansh Khanna, Tennant Company; University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
Shivansh Khanna
Tennant Company
University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
Shraddha Srivastava, Micron Technology, Boise, ID
Shraddha Srivastava
Micron Technology, Boise, ID